 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Watching your dog drag their butt across the floor, often referred to as “scooting,” can be both amusing and concerning. While many people assume worms are the culprit, there are actually several reasons why dogs might engage in this behavior. From itchy anal glands to dietary issues, scooting is often your dog’s way of communicating that something is wrong or uncomfortable. Understanding the potential causes behind this behavior can help you address the issue quickly and effectively, ensuring your furry friend stays happy and healthy.
Anal Gland Problems
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
One of the most common reasons for scooting is impacted or infected anal glands. These glands near the dog’s rectum release a scent when your dog defecates. However, if they become clogged or infected, it can cause discomfort and irritation, prompting your dog to drag their butt on the ground to relieve the itch. Regular check-ups with your vet and expressing your dog’s glands when necessary can help prevent this issue.
Allergies
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Just like humans, dogs can suffer from allergies, which may manifest in skin irritation, including around the rear end. Food allergies, environmental factors like pollen, or flea bites can cause itching and discomfort, leading to scooting. If your dog’s scooting is accompanied by licking or biting other areas of their body, allergies could be the culprit. Consulting your vet can help identify the allergen and find a treatment plan, such as antihistamines or a change in diet.
Parasites
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
While worms are a common concern, other parasites, such as fleas or mites, can also lead to scooting behavior. These pests can cause intense itching around your dog’s rear, leading them to drag their butt in an attempt to find relief. If your dog is scooting more frequently and you suspect parasites, checking for any visible signs like flea dirt or red, irritated skin is a good idea.
Dietary Issues
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Your dog’s diet significantly affects their overall health, including digestive function. If your dog isn’t getting enough fiber or if they are eating foods that cause gastrointestinal upset, it may lead to scooting. Fiber helps to firm up stool and allows the anal glands to express naturally during defecation. A diet lacking in fiber may result in loose stools and a higher likelihood of anal gland issues, leading to scooting.
Rectal Prolapse
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
In more severe cases, scooting may indicate a rectal prolapse. This occurs when part of the rectum protrudes from the anus, which can cause significant discomfort and irritation. This condition typically requires medical attention, and you may notice additional signs such as visible tissue protruding or blood. If your dog is scooting and showing other concerning symptoms, it’s essential to seek veterinary care immediately.
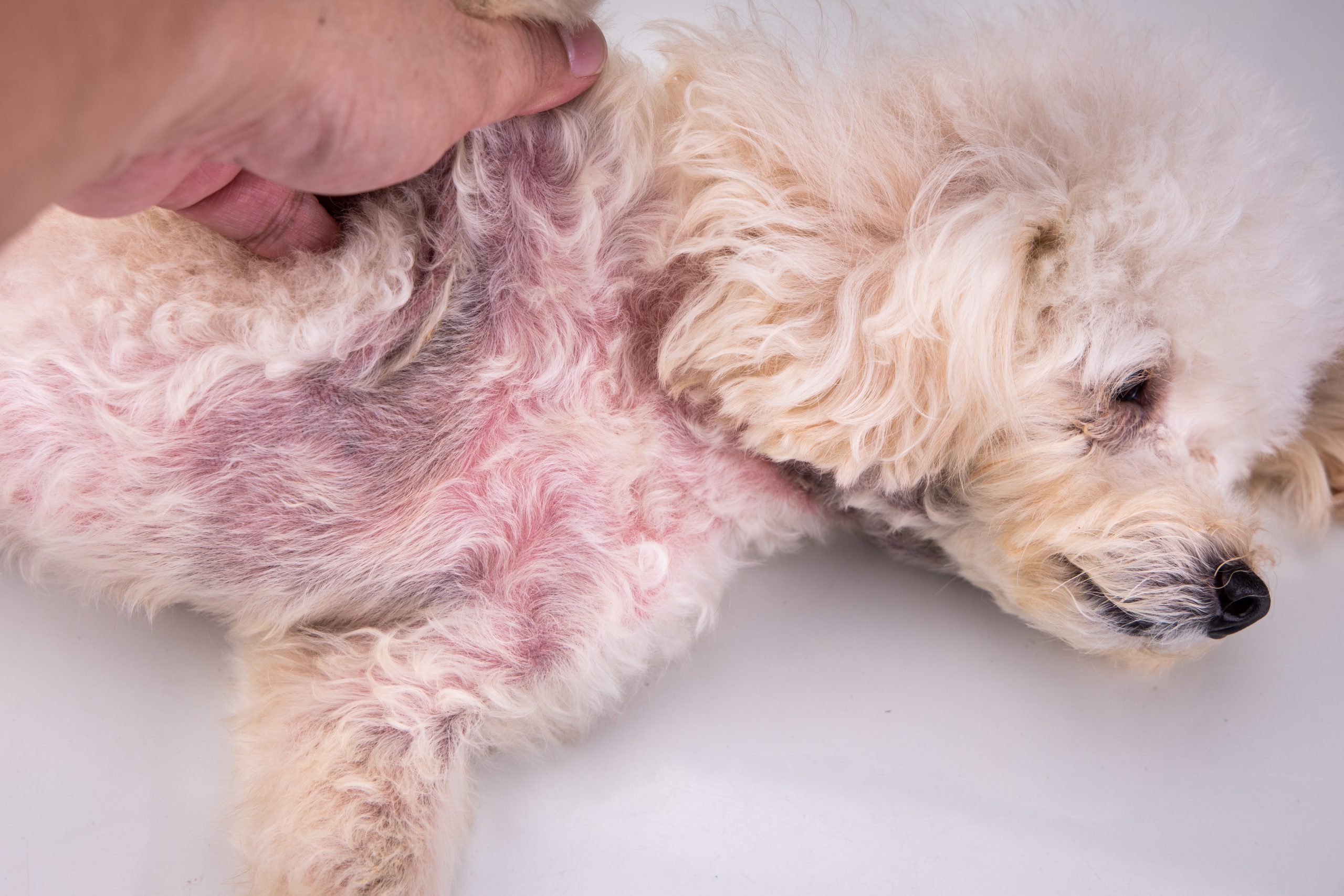
Skin Infections or Irritation
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Skin infections or general irritation around your dog’s rear can also cause scooting. This can be due to poor hygiene, excessive licking, or even leftover fecal matter in the fur. In some cases, fungal or bacterial infections may develop, causing intense itching and discomfort. Regular grooming and cleaning around your dog’s rear area can help prevent infections that may lead to scooting.
Full or Blocked Colon
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Dogs with constipation or a full colon may resort to scooting as a way to relieve pressure or discomfort. If your dog hasn’t been able to defecate properly, or if they have been straining to pass stool, the discomfort may cause them to drag their butt on the ground. Ensuring your dog has enough water, fiber, and exercise can help promote healthy bowel movements and prevent constipation-related scooting.
Anal Tumors or Growths
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Although less common, tumors or growths in the anal region can cause dogs to scoot as they try to relieve the discomfort. These growths can cause irritation or blockages, leading your dog to drag their rear across the ground. If your dog is scooting regularly and you notice any unusual lumps or swelling around the anus, it’s crucial to get them checked by a veterinarian for further evaluation.
Behavioral Issues
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Sometimes, scooting can be a behavioral issue rather than a medical one. Dogs may develop this habit out of boredom, anxiety, or as an attention-seeking behavior. Suppose your vet has ruled out any physical causes for the scooting. In that case, it may be worth considering behavioral training or increasing your dog’s mental and physical stimulation to reduce this behavior.
Post-Grooming Irritation
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
If your dog tends to scoot right after a grooming session, it could be due to irritation caused by shaving or trimming near their anal area. Clippers or scissors may cause slight abrasions or irritate the skin, prompting your dog to drag their butt to relieve the discomfort. Ensuring your groomer uses gentle methods around this sensitive area and using soothing wipes or balms afterward can help minimize post-grooming scooting.
The Real Reason Behind the Scoot
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
While scooting can be amusing, it’s often your dog’s way of telling you something is off. From anal gland issues and dietary problems to behavioral quirks, dogs have valid reasons for engaging in the “boot scoot boogie.” It’s not just for fun—it’s their way of seeking relief from discomfort or irritation. The next time you catch your dog scooting, remember that they may be trying to communicate a need for care or attention. Identifying the cause can help ensure your dog stays happy, healthy, and comfortable.

 1 month ago
8
1 month ago
8


















 English (US) ·
English (US) ·